Stroke Facts
Common Signs and Symptoms
 Any signs or symptoms below cause concern for stroke if all other possibilities are ruled out (example hypoglycemia).
Any signs or symptoms below cause concern for stroke if all other possibilities are ruled out (example hypoglycemia).
Sudden onset of one-sided weakness or numbness of face, arm, or leg
Sudden onset of visual disturbance
 Loss of speech, difficulty speaking or understanding speech
Loss of speech, difficulty speaking or understanding speech
Sudden onset of unilateral numbness
Symptoms of unexplained dizziness, falling, or loss of coordination
Sudden onset "Worse headache of my Life"
Risk Factors for Stroke
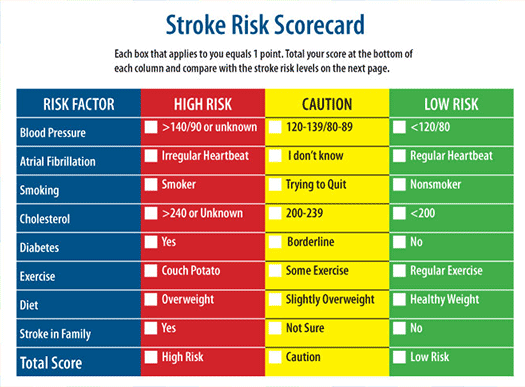 Modifiable Patients have some ability in preventing or controlling. Recent data shows 80% of strokes may be preventable if high BP, coronary heart disease, high cholesterol, atrial fibrillation, diabetes, smoking and weight are controlled or prevented.
Modifiable Patients have some ability in preventing or controlling. Recent data shows 80% of strokes may be preventable if high BP, coronary heart disease, high cholesterol, atrial fibrillation, diabetes, smoking and weight are controlled or prevented.
Not Modifiable risk factor are age, gender, race, personal and/or family history of stroke or TIA.
Types of Stroke
Ischemic Strokes: (~ 80- 85 %): Caused when a clot or fatty plaque blocks blood flow, starving cells of oxygen. Frequently no head ache but Focal Deficit- weakness on one side, difficulty speak or seeing.
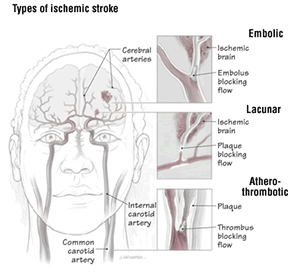 Embolic: (10-30%), a blood clot that forms elsewhere in the body and travels through the bloodstream to the brain.
Embolic: (10-30%), a blood clot that forms elsewhere in the body and travels through the bloodstream to the brain.
Thrombolic: (53%): The blood clot that triggers a thrombotic stroke, it usually forms inside an artery that already has been narrowed by atherosclerosis. This is a condition in which fatty deposits (plaque) build up inside blood vessels.
Lacunar : (20%): A stroke in a deep small vessel area of the brain (for example, a stroke in the thalamus, the basal ganglia or pons)
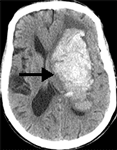 Hemorrhagic Strokes (10=15 %): Caused when a blood vessel leaks or breaks. Commonly presents with a headache.
Hemorrhagic Strokes (10=15 %): Caused when a blood vessel leaks or breaks. Commonly presents with a headache.
Intracerebral Hemorrhage: (ICH) Frequently from uncontrolled high blood pressure (50-80%).
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: (SAH) from aneurysm commonly present with "worse headache of my life".
28,000 Americans have ruptured aneurysms per year, and of the 28,000 aneurysms 50% die with first bleed. However of the 50% who do survive 1/3 have a major deficit, 1/3 have a moderate deficit, or 1/3 returns to normal
IU Health Methodist Comprehensive Treatments
Recanalization therapy in ischemic stroke: window of time for treatment: (From last seen normal to present time)
IU Health Methodist hospital is one of the few in the state that has this capabilty.
0 - 3 hrs (may be longer in a select group of patients): - IV t-PA
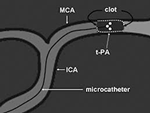 3 – 6 hrs Intra Arterial t-PA
3 – 6 hrs Intra Arterial t-PA
 0 – 8 hrs Mechanical interventional clot retriever and suction devices
0 – 8 hrs Mechanical interventional clot retriever and suction devices
Up to 12 hrs (24h) for posterior circulation acute ischemic stroke
Decompressive Hemicranectomy for massive swelling.
Hemorrhage: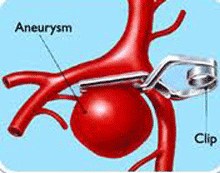 Bleeding due to aneurysms (hemorrhagic stroke) will get Clips or Coils of aneurysm.
Bleeding due to aneurysms (hemorrhagic stroke) will get Clips or Coils of aneurysm.
Clips: Open Craniotomy and placement of a clip.
Coils: Neuro-interventional intra-arterial femoral access and placement of coils.
“TIME LOST IS BRAIN LOST”
American Heart Association/American Stroke Association, Target Stroke 2011